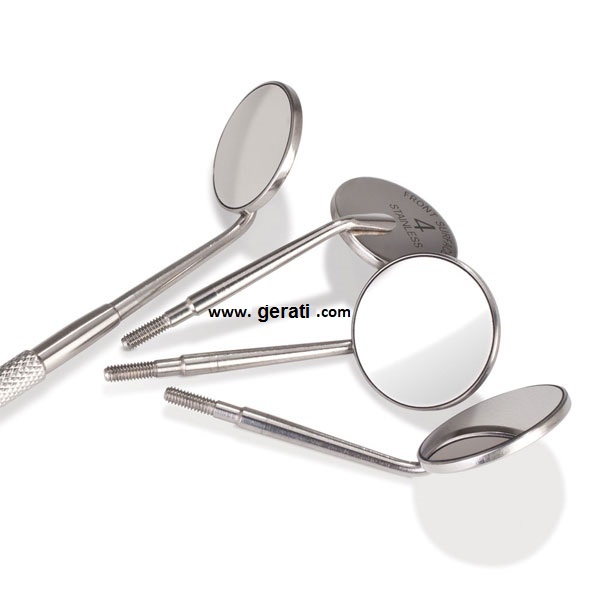
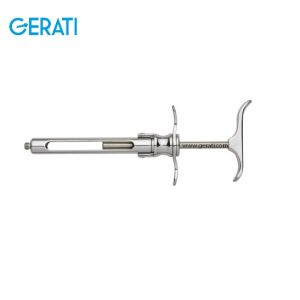
Dental Syringe
Dental Syringe. General Information
Dental anesthesia is the process of anesthetization for the purpose of operation on the dental, gingival, and its associated oral structures. The dental anesthesia procedure relieves the patients discomfort and pain during the dental treatment. Normally, the inferior alveolar nerve is anesthetized for dental anesthesia procedures. The usual site of injecting dental anesthesia is the mandibular foramen. This causes the blockage of the inferior dental nerve, causing the loss of sensation in the lower lip, chin, tongue and the teeth.
During the process of dental anesthetization, different anesthetic agents are used to block the inferior alveolar nerves sensory transmission to the central nervous system.
Topical anesthetics like Eugenol, benzocaine are applied to the oral tissues with a sterile swab to relieve buccal surface pain. Nitrous oxide, the anti-anxiety agent, relaxes the patient during the dental procedures. Anti-anxiety agents are used for moderate sedation purpose. Lidocaine, xylocaine, septocaine or marcaine, or any other suitable anesthetic agent, depending on the procedural requirement, induces local anesthesia. Deeper sedation or general anesthesia under ketamine or fentanyl may
be required in certain dental cases.
The dentist uses specialized dental syringe containing a breech-loading syringe that has an anesthetic solution packed in a hermetically sealed cartridge. The syringe tip is detachable from the syringe body. This dental syringe containing the anesthesia is inserted towards the root apex of the tooth until the bone is contacted. The dental carpule contains the anesthetic agent of xylocaine with epinephrine. The dental syringe may also contain an additional tool to supply water or air to remove debris while conducting the dental procedure. A 3-way dental syringe is used which can supply pressurized air, water, and a mist of water and air through separate channels to
assist the dental procedure.





Reviews
There are no reviews yet.